Other recent blogs
Let's talk
Reach out, we'd love to hear from you!
Ever since Google introduced the mobile-first indexing and mobile-friendly approach, Custom Mobile App Development has started gaining traction in the enterprise landscape. Companies are constantly on the lookout for cutting-edge mobile applications that can enable them to enhance customer experience and skyrocket business performance. The report by Allied Market Research Group predicts that the mobile application market will grow to reach $407.31 billion by 2026 at a CAGR of 18.4%.
Over the years, mobile devices and the applications that they have become more sophisticated, completely transforming the way we live and interact with our handheld mobile devices. Modern smartphones offer a wide range of functionality, such as allowing the users to access content on-the-go with the push of a button.
Mobile applications perfectly fit the bill for businesses looking to engage with their customers 24/7. Mobile apps also help brands develop a better understanding of their customers and plan their market strategies accordingly and build brand loyalty. However, getting a mobile application developed offers unique challenges for businesses, especially in choosing the type of mobile app that fits their specific use case and selecting the right Mobile App Development Services provider.
While looking for a suitable mobile app development partner, as a business owner, you’d often find yourself bombarded with a barrage of terminologies such as Native Apps, web apps, hybrid apps, and cross-platform apps. But how do you know which type of mobile application is best suited to your business needs? Although most of us are familiar with Android and iOS, it is critical to know the difference between native, web, hybrid, and cross-platform mobile apps.
Types of Mobile Apps by Technology
According to technology-wise categorization, mobile apps are of four broad types:
- Native Apps
- Web Apps
- Hybrid Apps
- Cross-Platform Apps
Different Types of Mobile Apps for Business – What to Choose?
- Native Apps
Native mobile applications are written specifically for a platform or operating system such as Android or iOS using a native-to-the-operating system language. For example, to develop a native Android app, you need to write the code in Java or Kotlin; similarly, for the iOS native app, the code is written in Swift or Objective-C.
Pros:- Native apps can extensively use the device’s hardware, such as the camera, GPS, microphone, compass, etc., and the operating system’s features.
- Native apps are highly performant, more reliable, more responsive, and deliver the ultimate user experience, which no other type of mobile app can match.
- Specifically developed for a platform with a singular focus, native apps are faster and more intuitive.
- Native apps leverage the device UI for delivering optimized customer experience.
- If your budget allows, native applications are the ideal choice.
- Native Mobile App Development is a future-proof investment
- The primary disadvantage of choosing a native app is that it comes with a high upfront cost of development.
- Compared to other app types such as hybrid, web, or cross-platform, a native app has the highest cost of ownership.
- The prominent factor that drives up the developmental cost of a native app is that you need to write different code for each platform.
- The code written for the Android platform is unusable for the iOS operating system.
- You need to build and maintain different versions and codebases of the app.
- You need to hire different coders for each platform at extra cost.
- A native app is also not suitable for businesses looking to achieve faster time-to-market.
- Every time there’s an update, the user needs to download and reinstall the app.
- Hybrid Apps
A hybrid app is a blend between a native app and a web application. In Hybrid Mobile App Development, the developers embed the mobile app’s code written in web development languages such as HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript into a native wrapper using plugins like Apache Cordova (Adobe PhoneGap) or Ionic’s Capacitor. Hybrid apps can download from app stores, just like native apps. Hybrid apps run from inside a native app and own embedded browsers using a WebKit such as WebView for Android and WKWebView for iOS.
Pros:- A hybrid app is much quicker to develop and cost-effective when compared to a native app.
- A hybrid app can serve as a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) before a business decides to build a native application.
- Hybrid mobile app development is more streamlined.
- Hybrid apps load fast and are ideal for countries with slow internet connections.
- Hybrid apps deliver consistent user experiences.
- The code, once written, is usable for multiple platforms.
- Perfect for apps that provide content.
- Since hybrid apps use a single code base, there is less code to maintain.
- The plugin system helps the app to access the platform’s features.
- Even though they look and feel like native apps, hybrid apps lack power and speed, considered as hallmarks of native apps.
- Achieving a great UX and navigation pattern is challenging in hybrid apps.
- Hybrid apps need to download various elements, which leads to higher load time.
- Hybrid apps can’t access all device features.
- Cross-Platform Apps
Cross-platform apps are those which run on multiple platforms. They have a much broader scope than hybrid apps and serve as a mid-mile solution between a native app and a hybrid app. In the fast-changing business ecosystem, more and more companies are adopting the Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) model, wherein the employees bring their own devices to work, ushering the demand for cross-platform mobile development to customize applications for running on different devices. Many consider hybrid and cross-platform apps as the same, but in reality, the only common thing between them is code sharability. A bulk of cross-platform mobile app development involves building the app with web technologies such as JavaScript, HTML5, and CSS.
Pros:- Developing A Cross-platform App requires less time in comparison to a native app.
- A single codebase is customizable for multiple platforms.
- Cross-platform apps deliver satisfactory performance and cross-platform support at an affordable cost.
- Cross-platform apps work well for games.
- Frameworks like React Native enable developers to build features like native UI, declarative programming, hot reloading, and modular architectures for a native-like app experience.
- Debugging cross-platform apps takes much longer than native apps, even with the availability of frameworks like Xamarin.
- Even cross-platform apps require some platform-specific native development.
- Projects with complex code and third-party integrations increase development time and cost.
- Another significant risk is with cross-platform security threats designed to deliver malicious files to multiple platforms.
- Web Apps
Mobile web app development involves leveraging web development languages such as HTML5, CSS, JavaScript, Ruby, etc., to build web applications that look and feel like native apps. Web apps are not standalone applications that need to be downloaded and installed on a mobile device. A web app is a responsive website that adapts itself to the user interface of the user’s device. When you install a web app, it merely bookmarks the URL on your device. Progressive Web App (PWA) is a kind of web app, which is a native app running inside a browser.
Pros:- Cater to a broad customer base across geographies providing services across multiple device types.
- Web apps bridge together the resourcefulness of the internet and the functionality of touchscreens.
- A single version website helps improve SEO.
- Adaptive web applications scale and fit to different screen sizes from tablets to smartphones.
- There is no need to customize web-based apps for a specific platform or OS, which means lower development costs.
- Web apps don’t require space in your mobile device.
- Users don’t need to download or update a web app from the app store.
- Web apps are entirely dependent on the browser used by the device, which means that the functionality supported by one browser might not be available in another browser.
- Since web apps are shells for websites, they can’t wholly work offline.
- Even if a web app has the option of offline mode, it still requires an internet connection to back up the data on the device, fetch new data, or refresh the screen.
- A web app may not always integrate with the device hardware.
- You can’t sell web apps through app stores.
How Progressive Web Apps and AMP Pages Work Great Together?
AMP stands for Accelerated Mobile Pages, which are stripped-down HTML copies of existing webpages that render quickly for static content. PWAs and AMP pages work great together to create compelling and super-fast user navigation. AMP pages can leverage many features of PWAs. The USP of AMP is the rapid delivery of content. Since a website’s Service Worker hinders the first load of PWAs, a good strategy is to have an AMP page as the entry point to your website and switch to the PWA for the onward journey. Re-using your AMP pages as data-source can dramatically reduce the complexities of backend development.
How to Choose Just One?
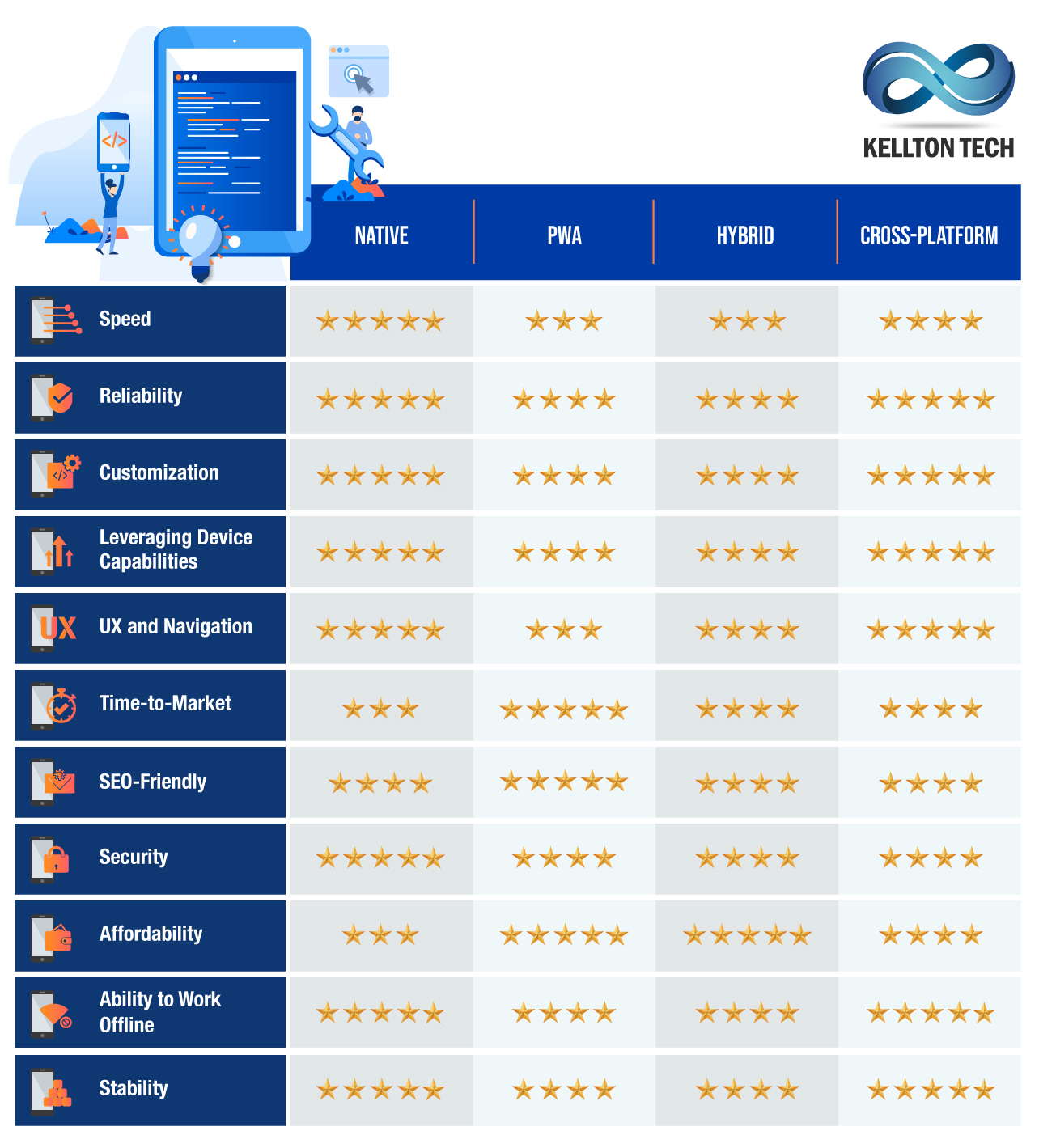
If you are looking to get a mobile app developed for your business, your choice of app type will depend on many factors. The following business needs should help you to choose the ideal mobile application.
- I Need a High-Performance Mobile App
The bottom line is that in terms of performance, no other app type can match the native app experience. Next, in terms of performance, are cross-platform apps, hybrid apps, and web apps. - I Need a Mobile App ASAP!
If a faster time-to-market is on the top priority of your business plan, native mobile app development cannot be the ideal choice for you. You should invest in building a web app, which takes the least time to develop and deploy. - I Have Limited Resources
If budget limitations constrain your business, you must consider getting a web app or a hybrid app built. Although the benefits of native mobile app development far outweigh its development cost, a hybrid app can serve as an MVP for your business to test waters. - My Business App Should Be Fast and Stable
If performance and functionality are your top business priorities, there is no way around it. All you need is a native app, as it gives you speed, stability, and customization, which are crucial for your success.
Recommended Reading: Mobile App Development: An essential guide for business executives






